Functions in Python are blocks of reusable code that perform a specific task.
They help make programs more organized, reduce repetition, and improve readability.
A function only runs when it is called, and it can also return data as a result.
Example:
def greet():
print("Hello, Python!")
greet()
Output:
Hello, Python!
Functions make your code:
Modular → break large programs into smaller parts
Reusable → use the same code multiple times
Organized → improves structure and readability
Easier to debug → fix issues in isolated sections
There are mainly two types of functions in Python:

Built-in Functions – Provided by Python (e.g., print(), len(), type(), range())
User-defined Functions – Created by the user to perform specific tasks
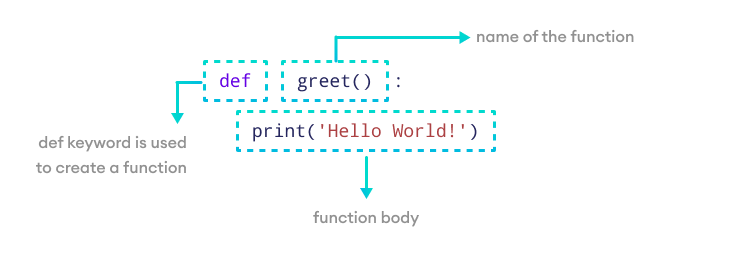
A function is defined using the def keyword followed by the function name and parentheses.
Syntax:
def function_name():
# code block
Example:
def welcome():
print("Welcome to Python Functions!")
welcome() # Function call
You can pass data (called arguments) into a function for processing.
Syntax:
def function_name(parameter1, parameter2):
# code block
Example:
def add(a, b):
print("Sum =", a + b)
add(5, 3)
Output:
Sum = 8
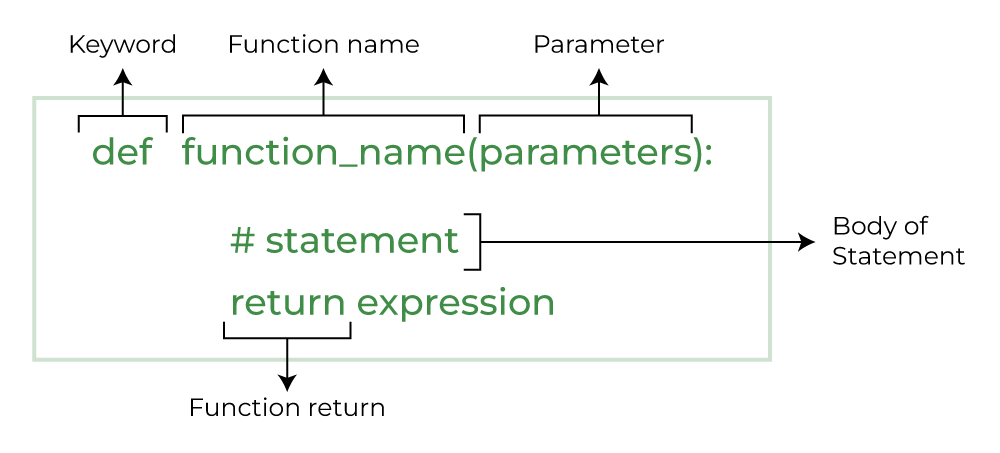
Sometimes you need the function to return a value instead of printing it directly.
Syntax:
def function_name(parameters):
return expression
Example:
def multiply(a, b):
return a * b
result = multiply(4, 5)
print("Product =", result)
Output:
Product = 20
You can assign default values to parameters.
If no argument is provided, the default value is used.
Example:
def greet(name="User"):
print("Hello,", name)
greet()
greet("Anuj")
Output:
Hello, User
Hello, Anuj
Python functions can return multiple values separated by commas.
Example:
def calculate(a, b):
sum = a + b
diff = a - b
return sum, diff
x, y = calculate(10, 5)
print("Sum =", x)
print("Difference =", y)
Output:
Sum = 15
Difference = 5
If you don’t know how many arguments will be passed, use:
*args → for multiple positional arguments
**kwargs → for multiple keyword arguments
Example 1: Using args
def total(*numbers):
print("Sum =", sum(numbers))
total(2, 4, 6)
Output:
Sum = 12
Example 2: Using kwargs
def display_info(**details):
for key, value in details.items():
print(key, ":", value)
display_info(name="Anuj", age=21, city="Dehradun")
Output:
name : Anuj
age : 21
city : Dehradun
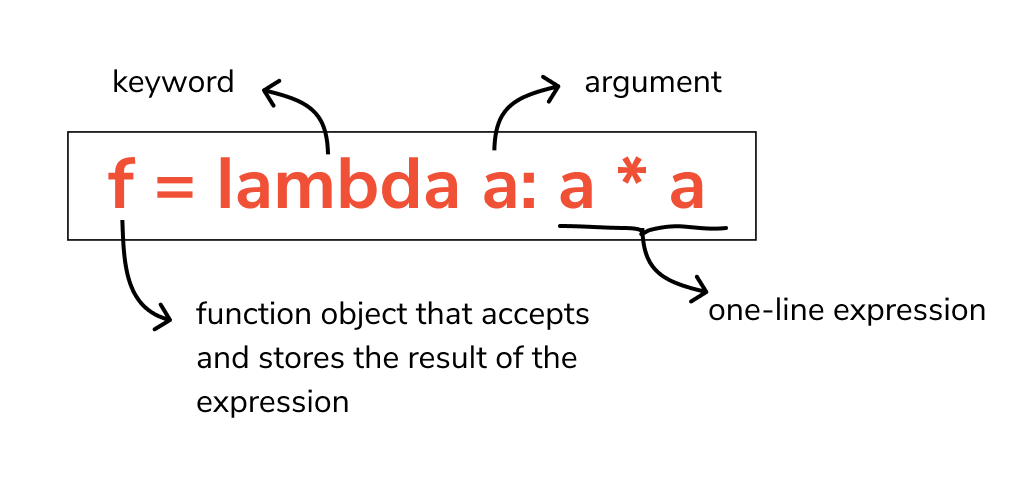
A lambda function is a small, one-line anonymous function used for short operations.
Syntax:
lambda arguments: expression
Example:
square = lambda x: x * x
print("Square =", square(5))
Output:
Square = 25
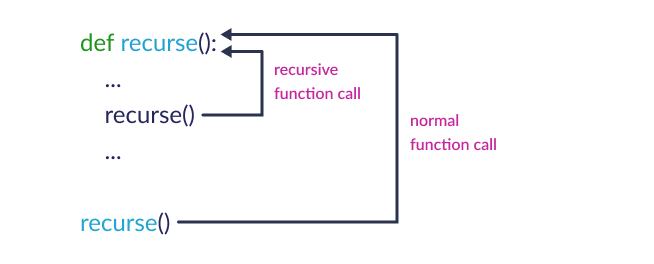
A recursive function calls itself until a condition is met.
Useful for tasks like factorial or Fibonacci series.
Example: Factorial using recursion
def factorial(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
else:
return n * factorial(n - 1)
print("Factorial =", factorial(5))
Output:
Factorial = 120
💡 Example 1: Even or Odd Checker
def check(num):
if num % 2 == 0:
print("Even")
else:
print("Odd")
check(7)
💡 Example 2: Area of Circle
def area_circle(radius):
return 3.14 * radius * radius
print("Area =", area_circle(5))
💡 Example 3: Simple Interest Calculator
def simple_interest(p, r, t):
return (p * r * t) / 100
print("Simple Interest =", simple_interest(1000, 5, 2))



