A Set is an unordered, unindexed, and mutable collection of unique elements.
Duplicate values are automatically removed.

✅ Example:
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry", "apple"}
print(fruits) # {'apple', 'banana', 'cherry'}
✅ Empty Set:
s = set() # ✅ Correct
s2 = {} # ❌ Creates an empty dictionary
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Unordered | No fixed position or index |
| Unique | Duplicate values are removed |
| Mutable | You can add/remove elements |
| Heterogeneous | Can store mixed data types |
✅ Example:
data = {10, "Sakshi", 9.4, True}
print(data)
Since sets are unordered, elements cannot be accessed by index or slicing.
✅ Example:
myset = {1, 2, 3}
for i in myset:
print(i)
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| add() | Add one element | s.add(5) |
| update() | Add multiple elements | s.update([6,7,8]) |
✅ Example:
nums = {1, 2, 3}
nums.add(4)
nums.update([5, 6])
print(nums) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| remove(x) | Removes element, raises error if not found | s.remove(2) |
| discard(x) | Removes element, no error if not found | s.discard(10) |
| pop() | Removes random element | s.pop() |
| clear() | Removes all elements | s.clear() |
✅ Example:
nums = {1, 2, 3, 4}
nums.remove(2)
nums.discard(5) # no error
print(nums)
Python supports mathematical set operations like union, intersection, difference, etc.
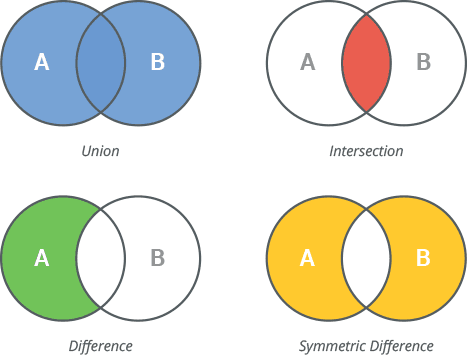
Let’s take:
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
| Operation | Symbol | Method | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Union | `A | B` | A.union(B) |
| Intersection | A & B | A.intersection(B) | {3,4} |
| Difference | A - B | A.difference(B) | {1,2} |
| Symmetric Difference | A ^ B | A.symmetric_difference(B) | {1,2,5,6} |
✅ Example:
print(A | B) # Union
print(A & B) # Intersection
print(A - B) # Difference
print(A ^ B) # Symmetric Difference
✅ Example:
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
print("banana" in fruits) # True
print("grape" not in fruits) # True
✅ Example:
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = A.copy()
print(B)
A frozenset is an immutable version of a set (cannot be changed after creation).
✅ Example:
A = frozenset([1, 2, 3])
# A.add(4) ❌ Error
print(A)
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| len() | Returns size | len(s) |
| max() | Largest element | max({1,3,2}) |
| min() | Smallest element | min({1,3,2}) |
| sum() | Sum of numeric elements | sum({1,2,3}) |
| sorted() | Returns sorted list | sorted(s) |
✅ Example: Remove duplicates from a list
nums = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5]
unique = set(nums)
print(unique) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}



