A dictionary is a collection of key–value pairs.
Each key is unique, and it maps to a specific value.
✅ Example:
student = {
"name": "Sakshi",
"branch": "CSE",
"sgpa": 9.4
}
✅ Accessing:
print(student["name"]) # Sakshi
print(student["sgpa"]) # 9.4
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Ordered (from Python 3.7+) | Keys maintain insertion order |
| Mutable | You can add/change values |
| Unique Keys | Duplicate keys not allowed |
| Dynamic | Can grow or shrink at runtime |
✅ Example:
# Method 1 – Using {}
person = {"name": "Riya", "age": 20, "city": "Dehradun"}
# Method 2 – Using dict() constructor
person = dict(name="Riya", age=20, city="Dehradun")
✅ Empty Dictionary:
data = {}
| Method | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Using key | student["name"] | "Sakshi" |
| Using get() | student.get("sgpa") | 9.4 |
| get() with default | student.get("roll", "Not Found") | "Not Found" |
✅ Example:
student = {"name": "Sakshi", "sgpa": 9.4}
print(student.get("branch", "CSE")) # default value if key not found
✅ Example:
student = {"name": "Sakshi", "sgpa": 9.4}
student["branch"] = "CSE" # Add new key
student["sgpa"] = 9.5 # Modify value
print(student)
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| pop(key) | Removes key & returns its value | student.pop("sgpa") |
| popitem() | Removes last inserted item | student.popitem() |
| del dict[key] | Deletes a key | del student["name"] |
| clear() | Empties the dictionary | student.clear() |
✅ Example:
student = {"name": "Sakshi", "branch": "CSE"}
student.pop("branch")
print(student) # {'name': 'Sakshi'}
✅ Example:
student = {"name": "Sakshi", "sgpa": 9.4, "branch": "CSE"}
for key in student:
print(key, ":", student[key])
✅ Other ways:
for key, value in student.items():
print(key, "=", value)
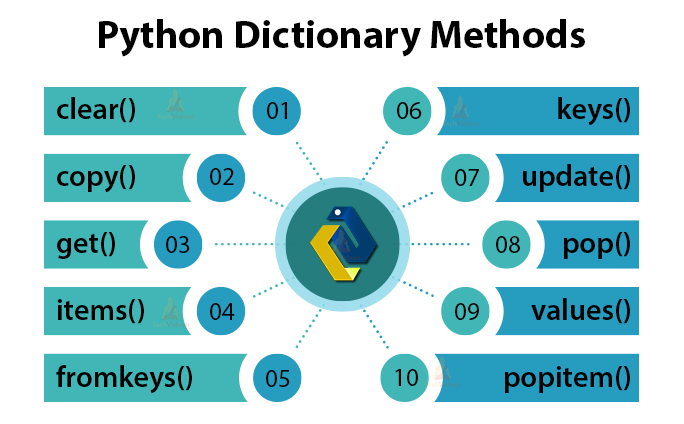
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| keys() | Returns all keys |
| values() | Returns all values |
| items() | Returns list of (key, value) pairs |
| update() | Merges two dictionaries |
| copy() | Returns shallow copy |
✅ Example:
student = {"name": "Sakshi", "sgpa": 9.4}
student.update({"branch": "CSE", "year": 3})
print(student)
A dictionary inside another dictionary.
✅ Example:
students = {
1: {"name": "Sakshi", "sgpa": 9.4},
2: {"name": "Riya", "sgpa": 8.9}
}
print(students[1]["name"]) # Sakshi
✅ Example:
squares = {x: x**2 for x in range(1, 6)}
print(squares) # {1:1, 2:4, 3:9, 4:16, 5:25}
✅ With condition:
even_squares = {x: x**2 for x in range(10) if x % 2 == 0}
print(even_squares)
✅ Example:
student = {"name": "Sakshi", "branch": "CSE"}
print("name" in student) # True
print("age" not in student) # True
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| len() | Number of key-value pairs | len(student) |
| str() | Converts to string | str(student) |
| type() | Returns type | type(student) |
✅ Example: Count character frequency
text = "banana"
freq = {}
for ch in text:
freq[ch] = freq.get(ch, 0) + 1
print(freq) # {'b':1, 'a':3, 'n':2}



